[ad_1]
A paper by Kogut (2024) has a nice overview of the organizations that develop pharmacy plan quality metrics. Pharmacy plan quality is vital since approximately 85% of the US population has prescription drug coverage through public (e.g., Medicare , Medicaid) or commercial (e.g., employer-provided) pharmacy plans. A helpful summary table is below.
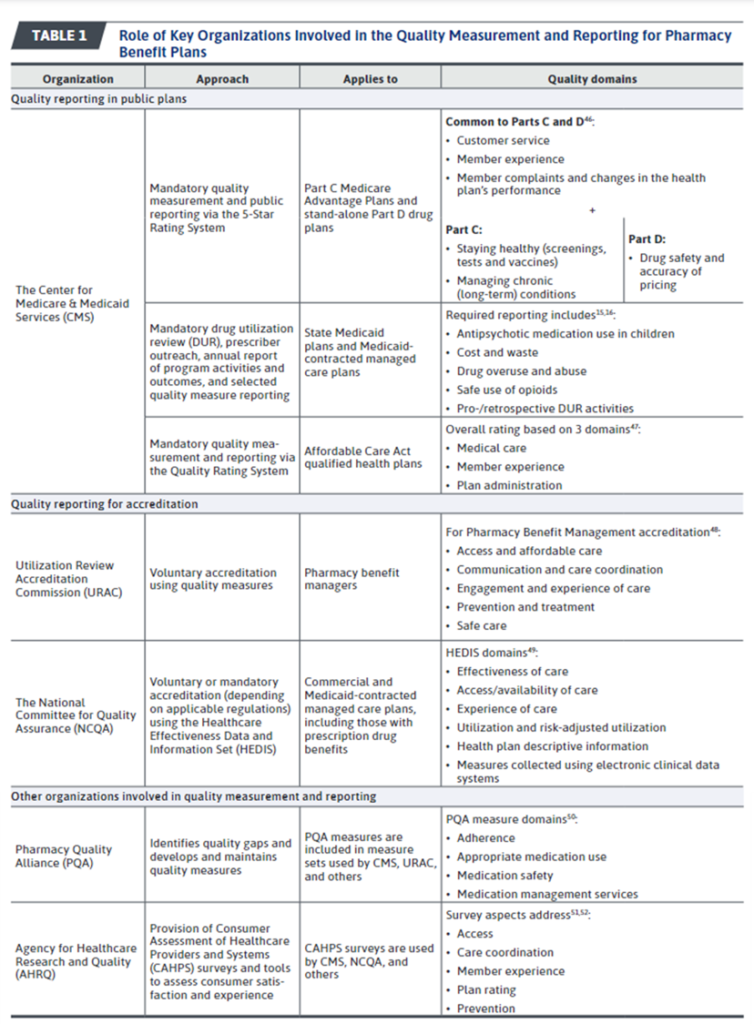
Quality measures are selected based on validity testing (to ensure that the measure accurately represents quality aspect intended be measured, reliability (to insure the measure is precise and estimate is done consistently), importance (i.e., aligns with key plan/population health priorities, usability (i.e., whether the metric is easily understood), feasibility (the burden imposed for data collection needed to estimate the measure), and consistency (whether it is consistent with other quality measures from other organization and also not duplicative of other quality measures).
Of note is recent legislation that impacts quality measurement for Medicaid plans.
Substance Use Disorder Prevention that Promotes Opioid Recovery and Treatment for Patients and Communities (SUPPORT) Act of 2018 introduced new requirements for state Medicaid DUR [drug utilization review] programs and Medicaid-contracted managed care plans. These requirements are designed to encourage the safe, effective, and efficient utilization of prescription opioids, with a focus on curbing overuse and misuse. Specific topics of quality measurement include monitoring the concur-rent use of prescription opioids with benzodiazepines or antipsychotics, ensuring appropriate opioid dosing and limiting the days’ supply, and identifying instances of suspected abuse. Additionally, the SUPPORT Act man-dated that Medicaid DUR programs monitor the use of antipsychotic medication in children.
One organization with which general (i.e., non-pharmacy) quality measure experts may be less familiar is Utilization Review Accreditation Commission (URAC).
URAC is the exclusive accreditation provider for pharmacy benefit management (PBM) companies that offer pharmacy benefit plans. Although URAC accreditation is voluntary, URAC-accredited PBMs represent more than 90% of prescription drug volume in the United States
More details on quality measurement–including how quality measure attribution is determined and how medication therapy management (MTM) are implemented–are available at the full article here.
[ad_2]
Source link



