[ad_1]
Here’s a complete list of keto words alphabetized for you. It’s the best keto glossary and a list of keto abbreviations so you can understand keto slang.
PLUS a quick keto FAQ.
If you are new here you may want to read the beginners guide to keto, how to start keto, and choose some delicious low-carb keto recipes.
Jump to:

What are keto acronyms?
A keto acronym (keto abbreviations) are the initials of a longer word, name, phrase, or sentence to make it easy to remember. For example, LCHF is the acronym for low-carb healthy-fat (or low-carb high-fat).
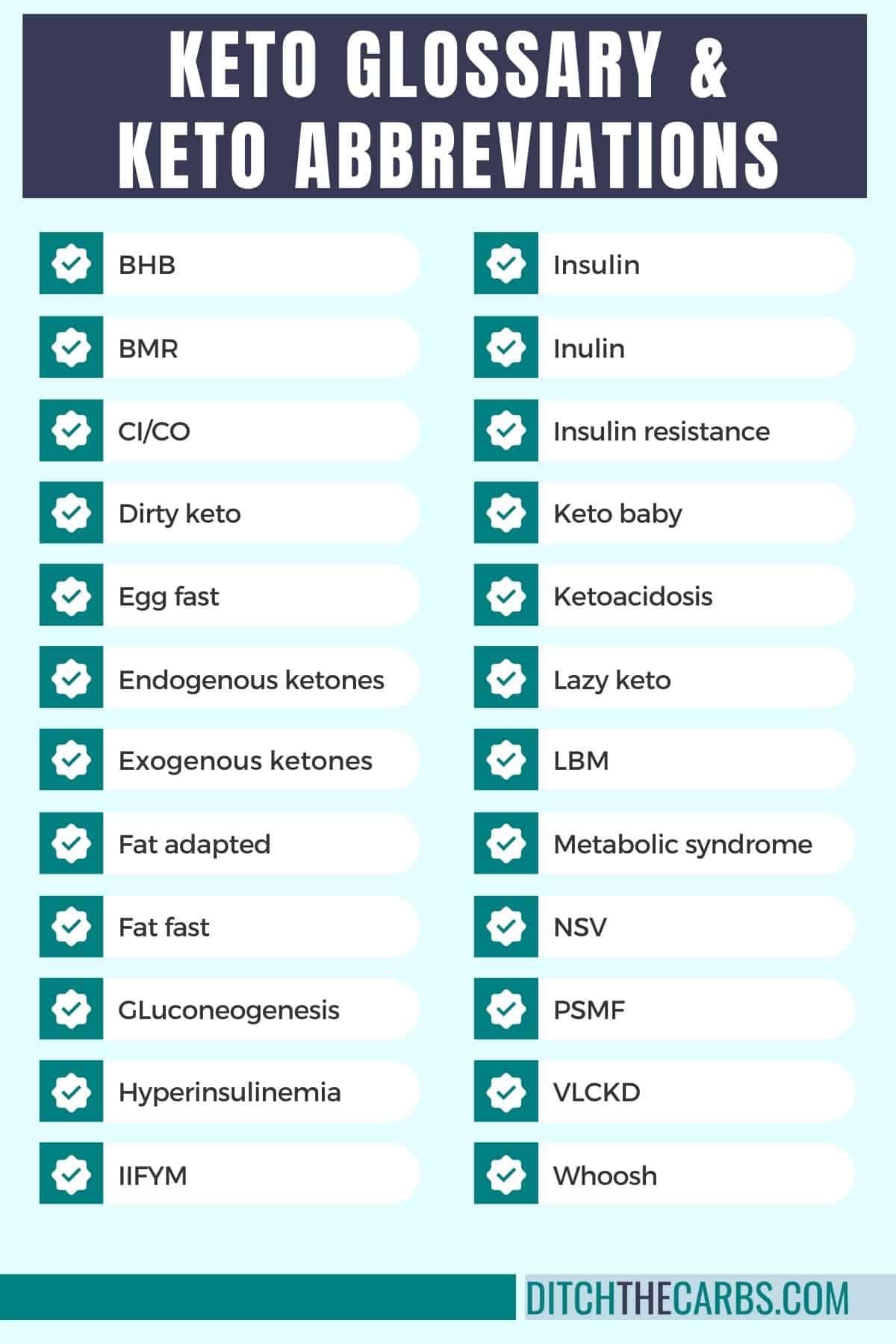
Keto diet glossary
The glossary is an alphabetized list of names, keto words, and terms with a short explanation. You could call this the keto dictionary.
Atkins diet
The Atkins diet was the first popular low-carb diet written by Dr. Roberty Atkins in the 1970s. The Atkins diet is characterized by 4 phases. Induction phase. Balancing phase. Fine-tuning phase. Maintenance phase.
Is Atkins the same as keto? In many respects, yes. Both diets encourage keto-friendly foods but the longer you are on the Atkins diet, you often slowly increase your carbs, you fine-tune your macros, and protein is not restricted.
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is an exogenous ketone produced by the liver when your body is burning fat. BHB is also a common keto supplement.
Blood glucose (BG)
Sugar is half glucose and half fructose.
Blood glucose (blood sugar) is a measurement of how much glucose is circulating in your blood.
Your basal metabolic rate (resting metabolic rate) is the minimum amount of energy your body requires when you are resting. It is the energy (or calories) you need to perform basic functions such as reparing cells, breathing, and pumping blood.
Carb counting
Whether you are on a keto diet, low-carb diet, or high-protein low-carb diet, you will begin carb counting to ensure you don;t go over your daily limit.
You can count carbs using a carb counting app or use a paper carb tracking food journal.
CI/CO
Calories in, calories are a measurement of how many calories have been consumed in the day compared to how many calories have been used via day-to-day living and exercise.
Clean keto
Clean keto is a ketogenic diet where only unprocessed whole foods are eaten. Keto shakes, keto bars, and keto takeouts are avoided.

Cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD)
A cyclical ketogenic diet is where you cycle (swap) through a strictly keto diet and higher carb days, “carb loading” days.
Dirty keto
This type of keto diet gives you more freedom on what you eat. If you are on the dirty keto diet, you only need to track your macronutrients but it doesn’t matter where those macronutrients come from. It could be junk food, processed foods, takeouts, keto shakes, and keto bars.
Egg fast
An egg fast is where you only eat a diet of eggs and some added fat. You can enjoy boiled eggs, fried eggs, scrambled eggs, poached eggs, and even egg salad. An egg fast is an easy protein and fat fast.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are salts and minerals. Electrolyte drinks often contain sodium, magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
You can buy electrolyte sachets or make homemade electrolyte drinks to help prevent keto flu.
Erythritol
Erythritol is the most common sweetener used in keto recipes to make them sugar-free. It is a sugar alcohol. Sugar alcohols are non-absorbable carbohydrates so are not included in net carbs. it is one of the many artificial sweeteners that are keto-friendly.
Endogenous ketones
Endo = from the inside. Exo = from the outside.
Endogenous ketones are ketones that are produced by the body. The most common is beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB).
Exogenous ketones (Ketone Esters and Ketone Salts)
Exogenous ketones are a keto supplement. They are manufactured and you buy them in a bottle.
Exogenous ketones (beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone) are claimed to boost athletic performances and are used as a treatment for neurological disorders including dementia, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy.
Exogenous ketones do not promote weight loss. Higher levels of ketones REFLECT fat loss but they do not CAUSE fat loss.
Fat adapted
When you have been on a ketogenic diet for some time, your body begins to use fat as its main fuel source instead of sugar and carbs. It takes time for your body to become fat-adapted to burn fat efficiently.
Fat bombs
Fat bombs are sugar-free high-fat snacks usually made with cream cheese, MCT oil, or coconut oil. You can have sweet fat bombs or savory fat bombs. They can curb your appetite without raising blood sugars.
Eating a fat bomb can stop sugar cravings. But you should only eat enough healthy fats to help control your appetite. Your fat intake is not a goal and does not need to reach a certain percentage. You want to burn your body fat, not fat from your food intake.

Fat fast (FF)
A fat fast is a diet that consists of mainly fat with minimum carbs and minimum protein. It kicks you into nutritional ketosis fast but is not sustainable due to the lack of protein and potential muscle loss.
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is the essential process of your body creating glucose from other substrates such as amino acids (from protein) and glycerol (from fat) in the absence of dietary or stored glucose.
Hyperinsulinemia (HI)
When the body is insulin-resistant, more insulin is required to lower and stabilize blood sugars to within the normal levels. The state of chronic high levels of insulin is called hyperinsulinemia.
IIFYM
“If it fits your macros” describes when you want to eat food that is higher carb but as long as it still fits within your daily carb limit and macros, you can eat it. It is very similar to the dirty or lazy keto diet.
Insulin
The hormone insulin is made in the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin helps the transportation of glucose into cells and reduces high blood sugar levels.
Inulin
Inulin is a prebiotic soluble fiber that is often used to sweeten keto foods.
Insulin resistance (IR)
Insulin resistance (IR) is a physiological condition where cells cannot respond normally to insulin. The cells have become resistant to insulin and so more insulin is required to regulate blood sugar levels.
Having chronic high levels of insulin may allow blood sugar levels to stay within the normal range and so delay the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes for many years.
Intermittent fasting (IF)
Intermittent fasting is an intentional period of not eating. Fasting is not starvation. There are many types of intermittent fasting methods. 16:8, 18:6, 5:2, and even the water fast.
Keto (ketogenic diet)
A keto diet is a way of eating when you restrict your carbohydrate intake to below 20g per day. You begin to fuel your body from protein and fat rather than burning carbs or sugar.
Once you live this way for a few weeks you will become fat-adapted and begin to lose weight and feel great along your keto journey.
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is not the same as nutritional ketosis. Nutritional ketosis is a very safe natural state when body fat is being burned and ketones are produced.
Ketoacidosis is often referred to as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is almost exclusively found in those with type 1 diabetes.
During ketoacidosis, glucose in the blood is extremely low and ketones are dangerously high. It is a dangerous health condition and can be fatal if not treated immediately.
Keto baby
Many women discover that their hormone imbalances are linked to insulin resistance, especially those with PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome). When they manage to reverse their resistance to insulin through a keto lifestyle their hormones often stabilize and they naturally become pregnant to make a keto baby.
Keto calculator
A keto calculator or macro calculator will calculate how many grams of carbs, fat, portion, and calories you need each day.
Keto flu
When you start a keto diet you may suffer from the keto flu. It is not the true flu but it gives you flu-like symptoms such as headaches, tiredness, lethargy, and nausea. You can help to prevent the keto flu by increasing your electrolytes and fluids.
Ketones
Ketones are made in the body from burning fat (endogenous ketones) or bought as a supplement (exogenous ketones). The most prevalent ketone the body makes is beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB). Ketones are a clean fuel that helps to fuel the body and brain.

Ketosis (nutritional ketosis)
Ketosis (or nutritional ketosis) is when our body burns fat. When fat is broken down the liver produces ketones which can be measured in the blood, the breath, and the urine.
Ketosis means you have ketone bodies circulating in your blood at levels above 0.4 mmol/liter.
Lazy keto
The lazy keto diet is similar to dirty keto. Lazy keto requires no cooking. It’s being able to reach your macros by buying ready-made food, keto bars, keto shakes, and takeouts.
Lean body mass (LBM)
This is your ideal body weight when you’re lean.
Low-carb healthy-fat (LCHF)
This is an easy way to describe the way of eating a variety of low-carb diets. Low-carb healthy-fat, or low-carb high-fat.
Macros (macronutrients)
There are 3 macronutrients. Fat, carbohydrates, and protein.
Medium chain triglycerides (MCT)
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCT) are saturated fats that are easily absorbed and easily converted into ketone bodies compared to long-chain triglycerides. MCT oil goes directly to the liver and is converted into ketones. MCT is found in coconut oil, lard, and butter.
Metabolic syndrome is a metabolic condition that includes obesity, type 2, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, lipid disorders, inflammation, and hypertension (high blood pressure).
Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA)
Monounsaturated fatty acids have ONE double carbon bond. This double bond is not saturated with hydrogen (hence the name monounsaturated). This double bond is unstable and can be broken and oxidized.
Monounsaturated fats are present in olive oil peanut butter, avocados, and even meat. MUFA are also found in duck, chicken, pork, and beef.
Non-scale victory (NSV)
A non-scale victory is a progress that is not reflected on the scales or by a reduction of body weight. It could be that you lose inches from your waist, or you can fit a smaller pair of jeans, but you didn’t lose any weight.
Another common NSV is improved and deeper sleep, improved skin, and reduced inflammation.
Paleo diet / primal diet
A paleo diet is based on what we think paleo prehistoric humans ate. Counting macros is not a huge part of those who follow the paleo diet or primal diet. This type of diet focuses on what they eat and did it exist in paleolithic times.
It is an evolutionary diet from the hunter-gatherer period and so the paleo diet and primal diet do not include milk as cows were not domesticated and farmed for their milk supply. They were killed for their meat. Foods like meat, eggs, nut, seeds, and berries are eaten.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)
The two main types of polyunsaturated fatty acids are Omega 3 and Omega 6. These are essential fatty acids that the body cannot make itself.
Omega 3 fatty acids are anti-inflammatory (oily fish, salmon, cod liver oil)), Omega 6 fatty acids are inflammatory (canola, soybean, rape seed oil). It is important to eat Omega 3:Omega 6 fatty acids in the ratio of 1:4.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids have many double bonds and are not saturated with hydrogen (hence the name polyunsaturated). These double bonds are unstable and can be broken and oxidized.
Protein fast
This is a diet that just consists of protein.

Protein sparing modified fast (PSMF)
A protein-sparing modified fast (PSMF) is a special low-carb and low-calorie diet that preserves muscle loss and promotes rapid weight loss.
The protein-sparing modified fast heavily restricts calories, fats and carbohydrates while increasing protein-rich foods.
Saturated fats (SFA)
Saturated fat is most commonly found in meats, heavy whipping cream, butter, ghee, tallow, eggs, coconut oil, and palm oil.
Saturated fats have no double carbon bonds and so are saturated with hydrogen. It is the most stable of fats, it has a longer shelf life, and a high smoke point.
Learn about healthy fats here.
Standard American diet (SAD)
SAD is an acronym for the standard American diet which is high-carb and high-fat with minimal whole food.
Standard ketogenic diet (SKD)
The standard ketogenic diet restricts carbohydrates to below 20g net carbs per day.
Total carbs vs net carbs
Net carbs are the total carbs minus fiber.
To calculate net carbs = total carbs minus fiber and sugar alcohols.
How much you restrict your carbohydrates is dependent on what you want to achieve and your health goals. It could be weight loss, to improve diabetic control, to improve sleep apnoea, to improve mood, to reduce blood pressure, or controlling epileptic seizures.
Type 1 diabetes (T1D)
Type one diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the pancreas reduces or stops producing sufficient insulin to lower high blood glucose levels.
Type one diabetes is not caused by eating too much sugar. It is an autoimmune disease where the beta cells in the pancreas stop or reduce how the body produces insulin.
Type 2 diabetes (T2D)
Type two diabetes is a reversible lifestyle disease. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and hyperinsulinemia.
Very low carb ketogenic diet (VLCKD)
A very low-carb ketogenic diet is similar to a ketogenic diet. You can achieve nutritional ketosis when you drop below 50g net carbs per day, but a VLKD cuts carbs further to below 20g net carbs per day.
Water fasting
Water fasting is a period of time when someone only drinks water and eats no food.
Way of eating (WOE)
This is an acronym for a person’s way of eating. It may refer to any type of diet.
Whoosh
The whoosh effect has two explanations.
1: When there is an initial rapid weight loss (whoosh) that is thought to be mainly water loss because you then stop losing weight and hit a plateau.
2: If you continue to eat a strict diet but the scales have stopped moving, often there is a delayed period then you begin to lose a lot of weight with a large whoosh.
Zero-carb diet
A zero-carb diet has no carbohydrates. It is a diet where you can only eat protein or fat.
Keto diet ingredients acronyms
- ACV – apple cider vinegar
- AS – artificial sweetener
- BPC – bulletproof coffee
- BPT – bulletproof tea
- CO – coconut oil
- HMC – heavy whipping cream
- EVOO – extra virgin olive oil


Keto FAQ
The keto diet is eating below 20 grams of net carbohydrates per day. It is a low-carb, high fat, moderate protein diet.
Generally these are regarded as the carb limits to aim for:
<100g/day = moderate low-carb
<50g/day = low-carb diet
<20g/day = keto diet
Glycogen is how the body stores excess glucose. If you reduce your sugar and carb intake you will utilize the glucose in your blood and then burn the glycogen. To replenish glycogen stores, as you eat again, your glucose levels will rise and glycogen will build up again in your liver and muscles
This is an acronym for high-intensity interval training. It is a series of short intense exercises followed by a short rest.
BMI is the acronym for body mass index. It is a calculation of a person’s height and weight but is inaccurate and out of date because it does not take into account if the weight is from fat or from muscle.
No, you can eat whatever meat you can afford, and whatever meat has the least processing and is raised in an ethical way. Grass-fed is reported to have a better Omega 3 essential fatty acid profile compared to grain-fed meat.

References:
[ad_2]
Source link


